Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Degenerative Disc Treatment
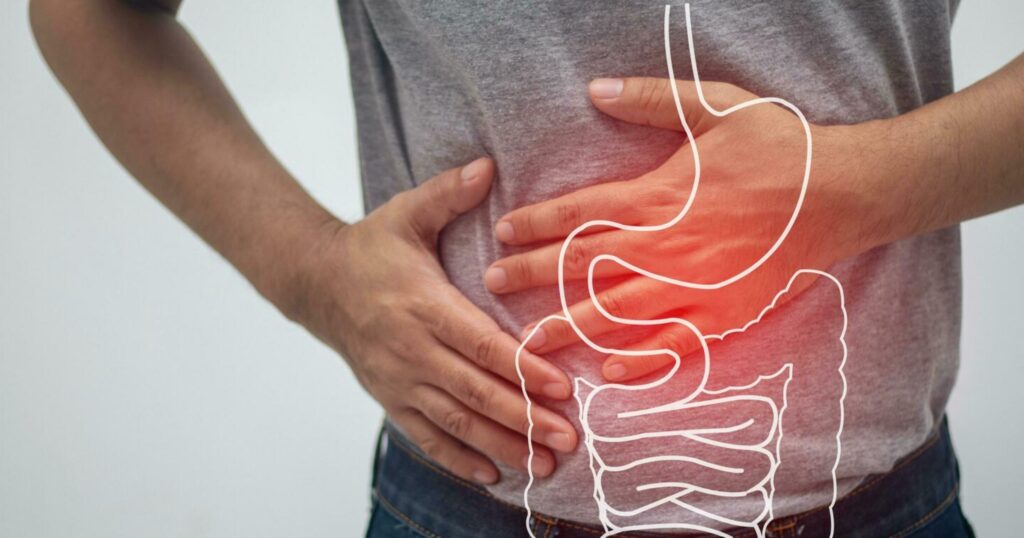
Are you suffering from low back pain caused by degenerative disc disease? Traditional therapies may have limited effectiveness, but there is hope on the horizon. Researchers at Mayo Clinic are exploring the potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in the treatment of degenerative disc disease, offering new possibilities for regenerative medicine.
Degenerative disc disease is a common condition characterized by the breakdown and deterioration of the intervertebral discs in the spine. This can lead to structural changes, instability, inflammation, and nerve ingrowth, causing significant low back pain and other symptoms.
While traditional therapies, such as lumbar fusion surgery, may provide temporary relief, their long-term effectiveness is variable. That’s where mesenchymal stem cells come in. These adult stem cells have the unique ability to differentiate into various cell types and possess regenerative properties.
Preclinical studies have shown promising results, demonstrating the effectiveness of MSCs in treating degenerative disc conditions in animals. Now, clinical trials are underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of MSCs in treating low back pain in humans. These trials, along with ongoing research on next-generation MSCs, hold the key to the future of stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease.
Key Takeaways:
- Mesenchymal stem cells show promise as a regenerative treatment for degenerative disc disease.
- Clinical trials are currently evaluating the safety and effectiveness of MSCs in treating low back pain.
- Next-generation MSCs and ongoing research offer exciting potential for the future of regenerative medicine.
- Traditional therapies for degenerative disc disease may have limited effectiveness and may decline over time.
- MSCs have the ability to repair damaged tissues, modulate inflammation, and stimulate tissue regeneration.
The Global Burden of Low Back Pain
Low back pain is a major health concern worldwide, with a significant impact on individuals, society, and the economy. Studies have shown that the global prevalence of low back pain is estimated to be between 26% and 42%. This indicates a substantial number of people affected by this condition.
Furthermore, the burden of low back pain extends beyond individual suffering. It has substantial economic implications, placing a strain on healthcare systems and the workforce. The cost of low back pain includes both direct and indirect expenses.
Direct healthcare costs refer to the expenses associated with diagnosing and treating low back pain. This includes diagnostic tests, medications, and rehabilitation services. Indirect costs, on the other hand, encompass the economic impact of low back pain on productivity and work absenteeism.
In the United States alone, the cost of low back pain was estimated to exceed $100 billion in 2006. This financial burden highlights the significant impact on society and the economy.
These statistics emphasize the need for effective strategies to address the global burden of low back pain. By understanding the prevalence and impact of this condition, policymakers, healthcare professionals, and researchers can collaborate to develop innovative solutions and improve outcomes for individuals affected by low back pain.
“Low back pain is a significant health issue affecting millions of people globally. Its impact extends beyond individual suffering, with substantial economic costs. By addressing the global burden of low back pain, we can improve the lives of millions and enhance societal and economic well-being.”
Understanding Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease is a common condition characterized by the breakdown and deterioration of the intervertebral discs in the spine. Although the exact cause of degenerative disc disease is not fully understood, it is believed to be influenced by genetic factors, aging, and environmental influences.
Disc degeneration can lead to various changes in the spine, including structural alterations, biomechanical instability, inflammation, as well as the growth of nerves and blood vessels. These changes can contribute to the development of low back pain and other symptoms associated with degenerative disc disease.
It is crucial to understand the underlying processes and mechanisms involved in the development and progression of degenerative disc disease in order to develop effective treatment strategies. By gaining insights into the pathogenesis of this condition, healthcare professionals can better tailor treatment approaches to alleviate pain and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by degenerative disc disease.
The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Degenerative Disc Treatment
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a type of adult stem cell that possess regenerative properties and hold great potential for the treatment of degenerative disc disease. These versatile cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types and exhibit remarkable regenerative capabilities.
MSCs can be sourced from different tissues in the body, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, synovium, periosteum, and cartilage. This accessibility makes MSCs an attractive option for regenerative medicine.
Studies have shown that MSCs can repair damaged tissues, modulate inflammation, and stimulate tissue regeneration through the release of paracrine factors and cell-to-cell interactions.
Excitingly, preclinical and clinical studies have provided evidence of the effectiveness of MSCs in improving pain and disability in patients with degenerative disc disease. These studies have demonstrated the regenerative potential of MSCs and their ability to promote tissue repair in the intervertebral discs.
“MSCs have emerged as a promising candidate for the treatment of degenerative disc disease due to their regenerative potential and ease of accessibility.”
Ongoing clinical trials are currently underway to further investigate the safety and efficacy of MSCs in treating degenerative disc disease. These trials involve larger patient populations and aim to provide valuable insights into the therapeutic potential of MSC-based treatments.
In conclusion, the regenerative properties of mesenchymal stem cells make them an exciting avenue for the treatment of degenerative disc disease. Their ability to repair damaged tissues and stimulate tissue regeneration offers hope for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life for patients suffering from this condition.
Clinical Trials and Research on MSCs for Low Back Pain
Mayo Clinic researchers, led by Dr. Wenchun Qu, are actively involved in multiple clinical trials evaluating the use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for the treatment of low back pain.
These clinical trials aim to assess the safety and efficacy of MSCs in larger patient populations and provide valuable data on the potential of stem cell therapy for low back pain.
Ongoing research is also focused on exploring the mechanisms of action of MSCs, optimizing treatment protocols, and developing next-generation MSCs with enhanced regenerative properties.
By studying the safety and efficacy of MSCs in clinical trials and advancing our understanding of their biological mechanisms, we can further support the potential of MSC therapy for low back pain and degenerative disc disease.
Advancements in Clinical Trials and Research
The clinical trials led by Dr. Wenchun Qu and his team at Mayo Clinic are a critical step in evaluating the safety and effectiveness of MSCs for low back pain treatment.
“Our goal is to provide reliable evidence on the use of MSCs for low back pain and contribute to the growing body of knowledge in regenerative medicine,” says Dr. Qu.
These trials involve carefully designed protocols with close monitoring of patients to ensure safety and accurate data collection.
Additionally, ongoing research efforts are focused on understanding how MSCs work, optimizing treatment protocols, and developing improved versions of MSCs with enhanced therapeutic potential.
The results of these studies and trials will provide valuable insights into the safety and efficacy of MSCs and further advance our understanding of their potential in treating low back pain and degenerative disc disease.
Ongoing Clinical Trials on MSCs for Low Back Pain
| Clinical Trial | Purpose | Number of Participants | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study 1 | Evaluate the safety and efficacy of MSCs in managing low back pain | 100 | Ongoing |
| Study 2 | Compare the outcomes of MSC therapy and traditional treatments for low back pain | 200 | Recruiting |
| Study 3 | Investigate the long-term effects of MSC therapy on low back pain | 50 | Completed |
These ongoing clinical trials involve a significant number of participants and aim to provide robust evidence on the safety and efficacy of MSCs for low back pain.
The table above provides a summary of some of the key clinical trials currently being conducted.
Efficacy of MSCs in Treating Low Back Pain
Multiple clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in providing pain relief and improving functional outcomes for patients with low back pain. These studies have shown significant reductions in pain scores and improvements in functional disability following treatment with MSCs.
In both short-term and long-term follow-up periods, patients have reported relief from low back pain and observed improved functionality. This highlights the potential of MSC therapy as a safe and effective treatment option.
The exact mechanisms of action by which MSCs provide pain relief and promote tissue regeneration are still being investigated. However, studies suggest that the paracrine factors and immunomodulatory properties of MSCs play a crucial role in reducing pain and facilitating tissue healing.
Dr. Li, a leading researcher in the field, emphasizes the positive impact of MSC therapy stating, “We have observed significant improvements in pain scores and functional outcomes in patients receiving MSC treatment for low back pain. This therapy has the potential to revolutionize the field of regenerative medicine.”
With their regenerative properties, MSCs show promise in relieving pain and improving functional outcomes for patients with low back pain. Further research and clinical trials are necessary to fully understand the long-term effects and optimize the efficacy of MSC-based treatments for low back pain and degenerative disc disease.
Safety and Adverse Events of MSC-Based Therapy
Patient safety is of utmost importance when it comes to the development and use of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-based therapies for low back pain. Clinical studies evaluating the safety of MSCs have shown encouraging results, with minimal adverse events reported. Most of these events are mild and transient in nature, causing little to no long-term effects.
Common adverse events associated with MSC-based therapy include localized pain at the injection site, temporary inflammation, and rare instances of allergic reactions. These events are generally well-tolerated and can be effectively managed by healthcare professionals.
“The safety profile of MSC-based therapy is reassuring, with minimal adverse events observed in clinical studies.”
Despite the overall positive safety profile, continued research is essential to fully understand the long-term effects and potential risks of MSC-based therapies. Rigorous quality control measures, standardized treatment protocols, and close monitoring of patients are paramount to ensuring the safety and efficacy of these innovative treatment options.
Promoting Safety in MSC-Based Therapies
To ensure patient safety, healthcare professionals and researchers follow stringent regulations and guidelines for the development and administration of MSC-based therapies:
- Adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for the production and quality control of MSCs
- Standardization of injection techniques and treatment protocols
- Thorough evaluation of patient eligibility and suitability for MSC-based therapy
- Close monitoring of patients during and after treatment to detect and manage any adverse events
The commitment to safety combined with ongoing research efforts will continue to advance the field of MSC-based therapy and ensure the well-being of patients seeking these innovative treatment options.
Future Prospects of MSC Therapy for Degenerative Disc Disease
The field of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy for degenerative disc disease holds great promise for the future of regenerative medicine. Ongoing research aims to optimize MSC-based treatments, develop next-generation MSCs with enhanced regenerative properties, and explore new therapeutic approaches.
Advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials may further enhance the effectiveness of MSC therapy by providing scaffolds and growth factors that support tissue regeneration. The combination of MSCs with these innovative technologies has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of low back pain caused by degenerative disc disease.
Additionally, advancements in cell manufacturing and delivery methods can improve the safety, scalability, and accessibility of MSC-based treatments. These developments may allow for more efficient and widespread use of MSC therapy in clinical settings, benefiting patients worldwide.
Advancements in Tissue Engineering and Biomaterials
Tissue engineering and biomaterials play a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness of MSC therapy. Researchers are actively working on developing scaffolds and biomaterials that mimic the natural environment of the intervertebral disc and promote tissue regeneration.
By providing structural support and releasing growth factors, these biomaterials can create an optimal environment for MSCs to differentiate into disc-like cells and facilitate the repair and regeneration of degenerated discs. The integration of tissue engineering approaches with MSC therapy has the potential to provide long-lasting and durable outcomes for patients with degenerative disc disease.
Advancements in Cell Manufacturing and Delivery Methods
Advancements in cell manufacturing and delivery methods are also being explored to improve the safety, scalability, and accessibility of MSC-based treatments for degenerative disc disease. Researchers are focusing on optimizing the production of MSCs, ensuring their quality and consistency in large-scale manufacturing processes.
Furthermore, innovative delivery methods, such as minimally invasive injection techniques or scaffold-based approaches, are being investigated to precisely target the affected disc and enhance the retention of MSCs within the disc tissue. These advancements can improve treatment outcomes and minimize the invasiveness of the procedure, leading to better patient experiences.
Exploring New Therapeutic Approaches
Beyond optimizing current MSC therapy approaches, researchers are also exploring new therapeutic strategies for degenerative disc disease. This includes investigating the use of combinatory approaches, such as combining MSCs with other cell types or therapeutic agents, to enhance the regenerative potential and effectiveness of MSC therapy.
Additionally, advancements in gene editing technologies hold promise for the development of genetically modified MSCs that can exert more targeted and potent regenerative effects on degenerated discs. These next-generation MSCs, engineered to express specific growth factors or anti-inflammatory molecules, have the potential to further improve treatment outcomes and accelerate the healing process.
| Advancements | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Optimization of MSC-based treatments | Improved efficacy and patient outcomes |
| Next-generation MSCs with enhanced regenerative properties | Greater potential for tissue repair and regeneration |
| Integration of tissue engineering and biomaterials | Creation of an optimal environment for tissue regeneration |
| Advancements in cell manufacturing | Increase in safety, scalability, and accessibility of MSC therapies |
| Exploration of new therapeutic approaches | Potential for more targeted and potent regenerative effects |
In conclusion, the future of MSC therapy for degenerative disc disease is full of exciting possibilities. Advances in tissue engineering, cell manufacturing, and therapeutic approaches have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of low back pain and improve patient outcomes. With ongoing research and innovation, MSC-based treatments hold great promise for the future of regenerative medicine in addressing the challenges posed by degenerative disc disease.
Stem Cell Research and the Quest for Better Treatments
Stem cell research is at the forefront of regenerative medicine and is driving advancements in the quest for better treatments for degenerative disc disease. Scientists are exploring innovative approaches to enhance the therapeutic potential of stem cells and improve outcomes for patients.
Exploring New Cell Sources
Researchers are investigating new cell sources for regenerative treatments, such as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and amniotic stem cells. These unique cell types offer advantages for tissue regeneration and hold promise as potential treatment options for degenerative disc disease.
Innovative Approaches
In addition to exploring new cell sources, researchers are also investigating innovative approaches to enhance the effectiveness of stem cell therapy. Gene editing techniques and tissue engineering methods are being studied to optimize the regenerative potential of stem cells and improve their ability to repair and regenerate damaged discs.
Biomaterials and Growth Factors
The development of biomaterials, scaffolds, and growth factors that mimic the native disc environment is an active area of research in regenerative medicine. These advancements aim to create an optimal microenvironment for stem cells to promote tissue regeneration and repair.
Collaborations for Translation
Translating stem cell research into clinically viable treatments requires collaborations between researchers, clinicians, and industry partners. By working together, these stakeholders can accelerate the development and translation of stem cell-based therapies for degenerative disc disease, ultimately benefiting patients.
Advancements in Non-Surgical Treatment Options
While stem cell therapy shows promise for the treatment of degenerative disc disease, there are a variety of non-surgical treatment options available that play a crucial role in conservative management and the alleviation of low back pain.
Physical therapy, exercise programs, and rehabilitative interventions can significantly improve the strength and stability of the spine, enhance mobility, and reduce pain associated with degenerative disc disease. These conservative measures aim to address the root causes of the condition and help patients regain functional abilities.
Pain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and analgesics, may be prescribed to manage pain and reduce inflammation in individuals with degenerative disc disease.
In some cases, minimally invasive procedures can provide temporary relief from low back pain. Procedures such as epidural injections or nerve ablation may be considered to target specific areas and alleviate pain for short to medium durations.
It is important to note that the choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of symptoms and individual patient considerations. A shared decision-making approach between patients and healthcare professionals ensures that the treatment plan is tailored to meet the specific needs and goals of each patient.
Physical Therapy for Degenerative Disc Disease
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of non-surgical management for degenerative disc disease. It involves a comprehensive approach to address pain, functional limitations, and biomechanical imbalances associated with the condition. Physical therapists develop individualized exercise programs and rehabilitation strategies to improve posture and strengthen the supporting muscles of the spine.
These therapeutic exercises aim to:
- Stabilize the spine and reduce strain on affected discs
- Improve flexibility, range of motion, and joint mobility
- Enhance core strength and support
- Correct faulty movement patterns and posture
- Promote overall physical fitness and well-being
Physical therapy may also include other modalities such as manual therapy, joint mobilization, and therapeutic massage to relieve pain, reduce muscle tension, and improve tissue circulation.
The goal of physical therapy for degenerative disc disease is to empower individuals with the skills and knowledge to manage their condition, optimize their physical function, and improve their quality of life.
Conservative Management: A Holistic Approach
Non-surgical treatment options play a critical role in the conservative management of degenerative disc disease. These approaches not only provide relief from low back pain but also focus on improving spinal function, mobility, and overall well-being.
While stem cell therapy holds promise, it is important to acknowledge the benefits of non-surgical treatments and the positive impact they can have on the lives of individuals with degenerative disc disease. Physical therapy, pain medications, and minimally invasive procedures together form a comprehensive and holistic approach to managing the condition.
Through a combination of non-surgical treatment options, individuals with degenerative disc disease can effectively minimize pain, optimize their function, and maintain an active and fulfilling lifestyle.
| Treatment Options | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Physical therapy and exercise programs |
|
| Pain medications |
|
| Minimally invasive procedures |
|
Non-surgical treatment options for degenerative disc disease are effective, evidence-based approaches that can significantly improve the lives of individuals experiencing low back pain. While stem cell therapy holds tremendous potential for the future, it is crucial to recognize the value of conservative management in providing relief and optimizing functional outcomes.
Conclusion
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy holds promise as a regenerative treatment option for degenerative disc disease and low back pain. Both preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of MSCs in reducing pain and improving functional outcomes in patients with degenerative disc disease. The ongoing clinical trials and research efforts are dedicated to further investigating the safety, efficacy, and long-term effects of MSC-based therapies.
The future of MSC therapy for degenerative disc disease looks promising, with the potential for advancements in tissue engineering, biomaterials, and delivery methods. As researchers continue to explore the underlying mechanisms of MSCs and develop next-generation MSCs with enhanced regenerative properties, the treatment outcomes are likely to improve. These advancements not only offer hope for patients with degenerative disc disease but also hold the potential for revolutionizing the field of regenerative medicine.
While MSC therapy shows great potential, it is important to note that non-surgical treatment options, such as physical therapy and rehabilitative interventions, remain critical components of conservative management for degenerative disc disease. Collaborations between researchers, clinicians, and industry partners are crucial to ensure the translation of stem cell research into clinically viable treatments, ultimately improving the outcomes for patients suffering from degenerative disc disease.
FAQ
What is degenerative disc disease?
Degenerative disc disease is a common condition characterized by the breakdown and deterioration of the intervertebral discs in the spine. It can lead to low back pain and other symptoms.
Can mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) treat degenerative disc disease?
Yes, research has shown promising results in using MSCs for treating degenerative disc disease. MSCs have regenerative properties and can potentially repair damaged tissues in the discs.
Are there any ongoing clinical trials on MSCs for low back pain?
Yes, there are multiple clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of MSCs in treating low back pain. These trials aim to provide more evidence on the potential of stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease.
What are the potential benefits of mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
MSCs have the ability to reduce pain, improve functional outcomes, and stimulate tissue regeneration. They offer a potential alternative to traditional therapies and may provide long-lasting relief.
Are there any risks associated with MSC-based therapies?
Studies have reported minimal adverse events with MSC-based therapies, such as localized pain at the injection site and transient inflammation. Long-term effects and risks are still being studied.
What does the future hold for MSC therapy in degenerative disc disease?
Ongoing research aims to optimize MSC-based treatments, develop next-generation MSCs with enhanced regenerative properties, and explore new therapeutic approaches. The future looks promising for the treatment of low back pain.
What are some non-surgical treatment options for degenerative disc disease?
Non-surgical options include physical therapy, exercise programs, rehabilitative interventions, and pain medications. These treatments can help alleviate pain and improve mobility.
How does the global burden of low back pain impact individuals and society?
Low back pain is a major health concern worldwide, with significant healthcare costs, productivity loss, and disability. It affects individuals, society, and the economy.
What are the latest advancements in stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
Ongoing research is focused on improving MSC-based treatments, exploring new cell sources, and developing next-generation MSCs. Advances in tissue engineering and cell manufacturing methods are also being investigated.
Is stem cell therapy a replacement for traditional treatments of degenerative disc disease?
Stem cell therapy shows promise as a regenerative treatment option, but non-surgical treatments still play an important role in conservative management. The choice of treatment depends on individual factors and shared decision-making.
How effective are mesenchymal stem cells in treating low back pain?
Clinical studies have demonstrated significant reductions in pain and improvements in functional disability with MSC therapy. Both short-term and long-term benefits have been observed.
What is the role of mesenchymal stem cells in degenerative disc treatment?
MSCs have regenerative properties and can repair damaged tissues. They also possess immunomodulatory effects, which can help reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration.
What is the impact of degenerative disc disease on the spine?
Degenerative disc disease can cause structural changes, instability, biomechanical issues, inflammation, and the ingrowth of nerves and blood vessels in the spine. These changes contribute to low back pain and other symptoms.
How do mesenchymal stem cells work in treating degenerative disc disease?
MSCs release paracrine factors and interact with other cells to repair damaged tissues and modulate inflammation. They have the potential to regenerate disc tissues and provide pain relief.
What is the current research status on mesenchymal stem cells for low back pain?
Research is ongoing, with clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of MSCs in larger patient populations. Ongoing research aims to enhance the understanding of MSC therapy and develop better treatments.
What are the costs associated with low back pain?
Low back pain has substantial healthcare costs, productivity loss, and economic burden. In the United States alone, the cost of low back pain was estimated to exceed $100 billion in 2006.
How safe is mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have reported minimal adverse events with MSC therapy. Common adverse events include transient pain at the injection site and mild inflammation.
What are the future prospects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
The future of MSC therapy looks promising, with ongoing research on optimizing treatments, developing next-generation MSCs, and exploring new therapeutic approaches. The potential for advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials is also being explored.
How prevalent is low back pain globally?
Low back pain is a significant global health issue, with a prevalence ranging from 26% to 42% in the population.
Can stem cell therapy provide a long-term solution for degenerative disc disease?
While stem cell therapy shows promise, its long-term effects and durability are still being studied. Ongoing research aims to address these factors and improve the long-term outcomes of MSC-based treatments.
What are the benefits of mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
MSCs have regenerative properties and can repair damaged tissues. They also possess immunomodulatory effects, which can help reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration.
What is the effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cells in treating degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have demonstrated significant reductions in pain and improvements in functional disability with MSC therapy. Both short-term and long-term benefits have been observed.
What is the impact of degenerative disc disease on the spine?
Degenerative disc disease can cause structural changes, biomechanical instability, inflammation, and the ingrowth of nerves and blood vessels in the spine. These changes contribute to low back pain and other symptoms.
How do mesenchymal stem cells work in treating degenerative disc disease?
MSCs release paracrine factors and interact with other cells to repair damaged tissues and modulate inflammation. They have the potential to regenerate disc tissues and provide pain relief.
What is the current research status on mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
Research is ongoing, with clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of MSCs in larger patient populations. Ongoing research aims to enhance the understanding of MSC therapy and develop better treatments.
What are the costs associated with low back pain?
Low back pain has substantial healthcare costs, productivity loss, and economic burden. In the United States alone, the cost of low back pain was estimated to exceed $100 billion in 2006.
How safe is mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have reported minimal adverse events with MSC therapy. Common adverse events include transient pain at the injection site and mild inflammation.
What are the future prospects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
The future of MSC therapy looks promising, with ongoing research on optimizing treatments, developing next-generation MSCs, and exploring new therapeutic approaches. The potential for advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials is also being explored.
How prevalent is low back pain globally?
Low back pain is a significant global health issue, with a prevalence ranging from 26% to 42% in the population.
Can stem cell therapy provide a long-term solution for degenerative disc disease?
While stem cell therapy shows promise, its long-term effects and durability are still being studied. Ongoing research aims to address these factors and improve the long-term outcomes of MSC-based treatments.
What are the benefits of mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
MSCs have regenerative properties and can repair damaged tissues. They also possess immunomodulatory effects, which can help reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration.
What is the effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cells in treating degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have demonstrated significant reductions in pain and improvements in functional disability with MSC therapy. Both short-term and long-term benefits have been observed.
What is the impact of degenerative disc disease on the spine?
Degenerative disc disease can cause structural changes, biomechanical instability, inflammation, and the ingrowth of nerves and blood vessels in the spine. These changes contribute to low back pain and other symptoms.
How do mesenchymal stem cells work in treating degenerative disc disease?
MSCs release paracrine factors and interact with other cells to repair damaged tissues and modulate inflammation. They have the potential to regenerate disc tissues and provide pain relief.
What is the current research status on mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
Research is ongoing, with clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of MSCs in larger patient populations. Ongoing research aims to enhance the understanding of MSC therapy and develop better treatments.
What are the costs associated with low back pain?
Low back pain has substantial healthcare costs, productivity loss, and economic burden. In the United States alone, the cost of low back pain was estimated to exceed $100 billion in 2006.
How safe is mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have reported minimal adverse events with MSC therapy. Common adverse events include transient pain at the injection site and mild inflammation.
What are the future prospects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
The future of MSC therapy looks promising, with ongoing research on optimizing treatments, developing next-generation MSCs, and exploring new therapeutic approaches. The potential for advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials is also being explored.
How prevalent is low back pain globally?
Low back pain is a significant global health issue, with a prevalence ranging from 26% to 42% in the population.
Can stem cell therapy provide a long-term solution for degenerative disc disease?
While stem cell therapy shows promise, its long-term effects and durability are still being studied. Ongoing research aims to address these factors and improve the long-term outcomes of MSC-based treatments.
What are the benefits of mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
MSCs have regenerative properties and can repair damaged tissues. They also possess immunomodulatory effects, which can help reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration.
What is the effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cells in treating degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have demonstrated significant reductions in pain and improvements in functional disability with MSC therapy. Both short-term and long-term benefits have been observed.
What is the impact of degenerative disc disease on the spine?
Degenerative disc disease can cause structural changes, biomechanical instability, inflammation, and the ingrowth of nerves and blood vessels in the spine. These changes contribute to low back pain and other symptoms.
How do mesenchymal stem cells work in treating degenerative disc disease?
MSCs release paracrine factors and interact with other cells to repair damaged tissues and modulate inflammation. They have the potential to regenerate disc tissues and provide pain relief.
What is the current research status on mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
Research is ongoing, with clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of MSCs in larger patient populations. Ongoing research aims to enhance the understanding of MSC therapy and develop better treatments.
What are the costs associated with low back pain?
Low back pain has substantial healthcare costs, productivity loss, and economic burden. In the United States alone, the cost of low back pain was estimated to exceed $100 billion in 2006.
How safe is mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have reported minimal adverse events with MSC therapy. Common adverse events include transient pain at the injection site and mild inflammation.
What are the future prospects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
The future of MSC therapy looks promising, with ongoing research on optimizing treatments, developing next-generation MSCs, and exploring new therapeutic approaches. The potential for advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials is also being explored.
How prevalent is low back pain globally?
Low back pain is a significant global health issue, with a prevalence ranging from 26% to 42% in the population.
Can stem cell therapy provide a long-term solution for degenerative disc disease?
While stem cell therapy shows promise, its long-term effects and durability are still being studied. Ongoing research aims to address these factors and improve the long-term outcomes of MSC-based treatments.
What are the benefits of mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
MSCs have regenerative properties and can repair damaged tissues. They also possess immunomodulatory effects, which can help reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration.
What is the effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cells in treating degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have demonstrated significant reductions in pain and improvements in functional disability with MSC therapy. Both short-term and long-term benefits have been observed.
What is the impact of degenerative disc disease on the spine?
Degenerative disc disease can cause structural changes, biomechanical instability, inflammation, and the ingrowth of nerves and blood vessels in the spine. These changes contribute to low back pain and other symptoms.
How do mesenchymal stem cells work in treating degenerative disc disease?
MSCs release paracrine factors and interact with other cells to repair damaged tissues and modulate inflammation. They have the potential to regenerate disc tissues and provide pain relief.
What is the current research status on mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
Research is ongoing, with clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of MSCs in larger patient populations. Ongoing research aims to enhance the understanding of MSC therapy and develop better treatments.
What are the costs associated with low back pain?
Low back pain has substantial healthcare costs, productivity loss, and economic burden. In the United States alone, the cost of low back pain was estimated to exceed $100 billion in 2006.
How safe is mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have reported minimal adverse events with MSC therapy. Common adverse events include transient pain at the injection site and mild inflammation.
What are the future prospects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
The future of MSC therapy looks promising, with ongoing research on optimizing treatments, developing next-generation MSCs, and exploring new therapeutic approaches. The potential for advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials is also being explored.
How prevalent is low back pain globally?
Low back pain is a significant global health issue, with a prevalence ranging from 26% to 42% in the population.
Can stem cell therapy provide a long-term solution for degenerative disc disease?
While stem cell therapy shows promise, its long-term effects and durability are still being studied. Ongoing research aims to address these factors and improve the long-term outcomes of MSC-based treatments.
What are the benefits of mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
MSCs have regenerative properties and can repair damaged tissues. They also possess immunomodulatory effects, which can help reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration.
What is the effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cells in treating degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have demonstrated significant reductions in pain and improvements in functional disability with MSC therapy. Both short-term and long-term benefits have been observed.
What is the impact of degenerative disc disease on the spine?
Degenerative disc disease can cause structural changes, biomechanical instability, inflammation, and the ingrowth of nerves and blood vessels in the spine. These changes contribute to low back pain and other symptoms.
How do mesenchymal stem cells work in treating degenerative disc disease?
MSCs release paracrine factors and interact with other cells to repair damaged tissues and modulate inflammation. They have the potential to regenerate disc tissues and provide pain relief.
What is the current research status on mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
Research is ongoing, with clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of MSCs in larger patient populations. Ongoing research aims to enhance the understanding of MSC therapy and develop better treatments.
What are the costs associated with low back pain?
Low back pain has substantial healthcare costs, productivity loss, and economic burden. In the United States alone, the cost of low back pain was estimated to exceed $100 billion in 2006.
How safe is mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have reported minimal adverse events with MSC therapy. Common adverse events include transient pain at the injection site and mild inflammation.
What are the future prospects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
The future of MSC therapy looks promising, with ongoing research on optimizing treatments, developing next-generation MSCs, and exploring new therapeutic approaches. The potential for advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials is also being explored.
How prevalent is low back pain globally?
Low back pain is a significant global health issue, with a prevalence ranging from 26% to 42% in the population.
Can stem cell therapy provide a long-term solution for degenerative disc disease?
While stem cell therapy shows promise, its long-term effects and durability are still being studied. Ongoing research aims to address these factors and improve the long-term outcomes of MSC-based treatments.
What are the benefits of mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
MSCs have regenerative properties and can repair damaged tissues. They also possess immunomodulatory effects, which can help reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration.
What is the effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cells in treating degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have demonstrated significant reductions in pain and improvements in functional disability with MSC therapy. Both short-term and long-term benefits have been observed.
What is the impact of degenerative disc disease on the spine?
Degenerative disc disease can cause structural changes, biomechanical instability, inflammation, and the ingrowth of nerves and blood vessels in the spine. These changes contribute to low back pain and other symptoms.
How do mesenchymal stem cells work in treating degenerative disc disease?
MSCs release paracrine factors and interact with other cells to repair damaged tissues and modulate inflammation. They have the potential to regenerate disc tissues and provide pain relief.
What is the current research status on mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
Research is ongoing, with clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of MSCs in larger patient populations. Ongoing research aims to enhance the understanding of MSC therapy and develop better treatments.
What are the costs associated with low back pain?
Low back pain has substantial healthcare costs, productivity loss, and economic burden. In the United States alone, the cost of low back pain was estimated to exceed $100 billion in 2006.
How safe is mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have reported minimal adverse events with MSC therapy. Common adverse events include transient pain at the injection site and mild inflammation.
What are the future prospects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
The future of MSC therapy looks promising, with ongoing research on optimizing treatments, developing next-generation MSCs, and exploring new therapeutic approaches. The potential for advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials is also being explored.
How prevalent is low back pain globally?
Low back pain is a significant global health issue, with a prevalence ranging from 26% to 42% in the population.
Can stem cell therapy provide a long-term solution for degenerative disc disease?
While stem cell therapy shows promise, its long-term effects and durability are still being studied. Ongoing research aims to address these factors and improve the long-term outcomes of MSC-based treatments.
What are the benefits of mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
MSCs have regenerative properties and can repair damaged tissues. They also possess immunomodulatory effects, which can help reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration.
What is the effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cells in treating degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have demonstrated significant reductions in pain and improvements in functional disability with MSC therapy. Both short-term and long-term benefits have been observed.
What is the impact of degenerative disc disease on the spine?
Degenerative disc disease can cause structural changes, biomechanical instability, inflammation, and the ingrowth of nerves and blood vessels in the spine. These changes contribute to low back pain and other symptoms.
How do mesenchymal stem cells work in treating degenerative disc disease?
MSCs release paracrine factors and interact with other cells to repair damaged tissues and modulate inflammation. They have the potential to regenerate disc tissues and provide pain relief.
What is the current research status on mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
Research is ongoing, with clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of MSCs in larger patient populations. Ongoing research aims to enhance the understanding of MSC therapy and develop better treatments.
What are the costs associated with low back pain?
Low back pain has substantial healthcare costs, productivity loss, and economic burden. In the United States alone, the cost of low back pain was estimated to exceed $100 billion in 2006.
How safe is mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have reported minimal adverse events with MSC therapy. Common adverse events include transient pain at the injection site and mild inflammation.
What are the future prospects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
The future of MSC therapy looks promising, with ongoing research on optimizing treatments, developing next-generation MSCs, and exploring new therapeutic approaches. The potential for advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials is also being explored.
How prevalent is low back pain globally?
Low back pain is a significant global health issue, with a prevalence ranging from 26% to 42% in the population.
Can stem cell therapy provide a long-term solution for degenerative disc disease?
While stem cell therapy shows promise, its long-term effects and durability are still being studied. Ongoing research aims to address these factors and improve the long-term outcomes of MSC-based treatments.
What are the benefits of mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
MSCs have regenerative properties and can repair damaged tissues. They also possess immunomodulatory effects, which can help reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration.
What is the effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cells in treating degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have demonstrated significant reductions in pain and improvements in functional disability with MSC therapy. Both short-term and long-term benefits have been observed.
What is the impact of degenerative disc disease on the spine?
Degenerative disc disease can cause structural changes, biomechanical instability, inflammation, and the ingrowth of nerves and blood vessels in the spine. These changes contribute to low back pain and other symptoms.
How do mesenchymal stem cells work in treating degenerative disc disease?
MSCs release paracrine factors and interact with other cells to repair damaged tissues and modulate inflammation. They have the potential to regenerate disc tissues and provide pain relief.
What is the current research status on mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
Research is ongoing, with clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of MSCs in larger patient populations. Ongoing research aims to enhance the understanding of MSC therapy and develop better treatments.
What are the costs associated with low back pain?
Low back pain has substantial healthcare costs, productivity loss, and economic burden. In the United States alone, the cost of low back pain was estimated to exceed $100 billion in 2006.
How safe is mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have reported minimal adverse events with MSC therapy. Common adverse events include transient pain at the injection site and mild inflammation.
What are the future prospects of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease?
The future of MSC therapy looks promising, with ongoing research on optimizing treatments, developing next-generation MSCs, and exploring new therapeutic approaches. The potential for advancements in tissue engineering and biomaterials is also being explored.
How prevalent is low back pain globally?
Low back pain is a significant global health issue, with a prevalence ranging from 26% to 42% in the population.
Can stem cell therapy provide a long-term solution for degenerative disc disease?
While stem cell therapy shows promise, its long-term effects and durability are still being studied. Ongoing research aims to address these factors and improve the long-term outcomes of MSC-based treatments.
What are the benefits of mesenchymal stem cells for degenerative disc disease?
MSCs have regenerative properties and can repair damaged tissues. They also possess immunomodulatory effects, which can help reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration.
What is the effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cells in treating degenerative disc disease?
Clinical studies have demonstrated significant reductions in pain and improvements in functional disability with MSC therapy. Both short-term and long-term benefits have been observed.
Source Links
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/medical-professionals/physical-medicine-rehabilitation/news/evaluating-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-mesenchymal-stem-cells-in-the-treatment-of-low-back-pain/mac-20543434
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10219191/
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2023.1155357